New Uzbekistan is a state where the highest value is a person and the interests of the people.
By Yusupov Umid Sobirzhanovich
PhD in Economics, assistant professor
The following article by the above writer has been contributed by the Embassy of the Republic of Uzbekistan in Seoul to The Korea Post media for publication, which publishes 3 English and 2 Korean-language news publications since 1985.—Ed.
Against the backdrop of global challenges, world market conditions and the rapidly changing situation associated with cataclysms and the pandemic, the issues of reducing poverty and improving the well-being of the wide strata of population are priorities for almost every country. In its turn, the effectiveness of the taken measures and managerial decisions largely depends on the adequacy and the suitability of the implemented socio-economic policy model to the realities of a particular state.
In the modern science and practice, a considerable number of models of socio-economic policy are being examined, what is caused by the variety of criteria, according to which the so-called "welfare states" are classified:

-significance (priority level) of the social policy among other policies (liberal, conservative, etc.);
-distribution of social functions between the state and the private sector;
-the security level (in the broad sense – financial and social services) of citizens (mainly, the wide strata of population);
-priority tasks (tactical and strategic) of the state in the field of social development.
As a rule, "welfare states" administer a social market economy. By definition, a social market economy is an economic system organized on the basis of market self-regulation, in which the coordination of actions is carried out on the basis of interaction in the markets of free private producers and free individual consumers. The social market economy model lies on the requirement that neither the state nor the private business have the right to have full control over the economy, but rather must serve the people. In this kind of a mixed economy, just as in a market economy, only the decisions of the consumers themselves, the resource providers and the private firms determine the structure of resource allocation. However, at the same time, the economically stronger ones are obliged to support the weaker. The role of the state is to develop the sense of mutual responsibility of all participants in the market and to correct unfair trends in competition, trade and income distribution. This system is seen as an alternative to a "pure capitalism" and an "absolute socialism".
The concept was started to be realized by Ludwig Erhard (the Minister of Economics, and later the Federal Chancellor of the Federal Republic of Germany). The name of the social market economy system was given in 1946 by the economist Alfred Müller-Armac. The concept received support from the Social Democrats.
The main characteristics of the social market economy model:
-ensuring full employment of the population;
-social security, social justice, and social progress (by carrying out redistribution measures by the state in the form of social assistance, social pensions and equalization payments, subsidies, grants, a progressive income tax scale, etc., through the social security system: pension and medical insurance, unemployment and care insurance, accident insurance; through labor and social legislation);
-private ownership of the means of production, and free pricing;
-creating conditions for competition and ensuring competition (for example, through antitrust laws, and laws against unfair competition);
-conscious policy of strengthening the economic growth environment;
-stable currency policy (including through an independent issuing bank);
-freedom of foreign trade and foreign exchange.
At the same time, the basic components of the social state of "general welfare" have been reformed and function with varying degrees of success.
These include institutions of education, healthcare, employment, social security, social protection of population. In addition, there is a system of social guarantees that strives to ensure a standard of living not below the poverty line. This is facilitated by a number of social policy measures, such as equating the minimum wage to the subsistence level.
Thus, each model of the socio-economic policy has its own advantages and disadvantages. Some of them have even turned out to be destructive and have shown negative (up to the destruction of statehood) consequences of their implementation. For example, in such countries as Libya and Venezuela, despite the availability of the sufficient natural resources (more precisely, minerals) for progressive development, the instruments of state social and economic policy could not be effectively combined.
The Republic of Korea can be attributed to the number of countries that have developed their own method of effective combination of the liberal economy (in conditions of the virtual absence of natural resources) and social policy instruments.
For example, since the beginning of the Covid-19 pandemic this socio-economic system has shown its viability in practice. In particular, on March, 17, 2020, the Law on Amendments to the Budget for the Year 2020 was approved; additional budget expenditures for the implementation of the anti-crisis plan in the amount of 10.9 trillion won (about $13 billion) were approved.
Immediate actions were taken for the mass testing of the population for coronavirus (including those without coronavirus symptoms), for additional funding of the medical institutions and for the provision of the measures related to quarantine (2.3 trillion won). The provision of temporary allowance to cover the basic living expenses of the population, including people that are in self-isolation regardless of the result of testing for coronavirus; the introduction of the consumer cards for the low-income households, subsidies for the payment of the parental benefits and the retraining of the citizens, who have lost their jobs due to the coronavirus, have significantly mitigated the negative consequences of the first pandemic wave and proved the effectiveness of the state's socio-economic policy, as well as a fairly high level of the social cohesion.
Within this context, it should be noted that numerous countries have turned the peculiarities of their social organization and even of culture into the important advantages of their national economy. In this vein, the main social features of Uzbekistan and the population of the country are:
-the transition from functioning under the command-administrative form of economic relations to the system of social and market relations, and the consequences of this transition;
-openness to modern financial-economic innovations, conservatism towards social and living changes;
-industriousness with a relatively low level of self-organization;
-intolerance towards social injustice;
-progressive social stratification with the strong social support for the underprovided from the state and the society;
-preservation of irrational bureaucracy in the face of the real actions of the authorities to eliminate the "managerial arrogance" and paperwork.
It should also be noted that resulting transformations over the past five years, the standard of living of people has increased, the growth of the country's economy has reached 24%, industry – 34%, export has increased 1.5 times, foreign investment – 3 times. The average monthly salary has increased by 2.2 times. Our task is to increase the gross domestic product per capita by 1.6 times in the next 5 years. By 2030, per capita income will have been raised up to $4,000, thus, creating a solid foundation for joining the ranks of the upper middle income countries.

New Uzbekistan - is a society and a state where the highest value is a person and the interests of the people. Shavkat Mirziyoyev, winner of the Presidential election, meets with voters on October 2021in Tashkent.
At the same time, it is widely known that the macroeconomic growth does not always lead to the socio-economic development. This requires the synchronous development of the economic and the social systems, designed to serve, first of all, the interests of the citizens of the country.
On this basis, the President of the Republic of Uzbekistan Sh.M. Mirziyoyev determined that:
Firstly, it is necessary to replace the previously existing principle of "state - society - person" with a new one – "person - society - state", and to fix it in the national legislation and the practice of law.
Secondly, in the process of the economic reforms, the main criterion should be the provision of human interests. This is the most important condition for the building of a truly people's state.
Thirdly, the constitutional consolidation of the role and the status of the civil society institutions, reflecting the principle “The society is the initiator of reforms”, is also a requirement of present time.
In this vein, it should be noted that the national interests are derived from the needs of the civil society. The spiritual, moral and intellectual potential of the society being a cohesive part of the population serves an intangible basis for the public-private partnership in the implementation of the economic interests of an individual and the society.
The mahalla has become the most progressive institution over the past five years in terms of the state financial support and empowerment. There are also real shifts in solving the social and living problems of the population, in increasing equity and targeting social assistance to the needy strata with the help of this and other institutions of the civil society. The belief that their quantitative growth (Figure No. 1.) will soon turn into a qualitative one fully has its grounds.
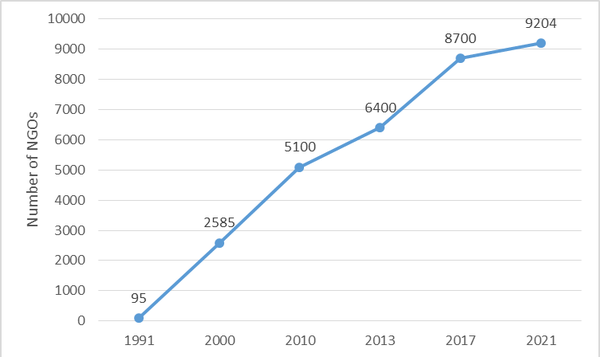
Due to the strong will and outstanding organizational potential of the President of the Republic of Uzbekistan Sh.M. Mirziyoyev, the tasks of ensuring the well-being of the people and reducing poverty were elevated to the rank of the state policy.
In particular, new approaches and methods have been developed to solve them. On the basis of the "iron", "women's", "youth" notebooks and the "notebook of mercy", specific plans and programs have been developed, which are being actively practically implemented today.
Precisely, in 2020, the Unified Register of the Social Protection system was established as a fundamentally new mechanism for working with the needy families, women and youth. Also, in order to identify "the points of growth" and to stimulate their development, the "mahallabai" system is being introduced. These mechanisms allow for the provision of the targeted material and non-material social assistance, which systematically expands its reach.
Thus, over the past period, due to the functioning of these systems, the employment was provided for 658 thousand (of which: 223.4 thousand – youth and 213.4 – women) out of 1.6 million unemployed able-bodied population.
The acuteness of the employment problem in Uzbekistan has at least two key aspects: the first, quantitative – the creation of the sufficient number of jobsites; second, qualitative – ensuring a decent level of wages and a social package.
Therefore, the mechanisms of social support are being developed in parallel through improving the system of self-employment. In particular, over the past period, out of 197.3 thousand, who had expressed a desire to learn the new professions and entrepreneurship, 170.2 thousand people have been trained.
In the search of unrealized infrastructure potential, 27.9 thousand empty non-residential premises, buildings and constructions were identified. Based on the results of studying the problems of the start-up entrepreneurs and the local farmers, assistance was provided in solving: 3.3 thousand problems related to the allocation of land and buildings; 3.5 thousand problems of connection to communication networks; 1.3 thousand problems in the sale of products and 47.9 thousand problems associated with the allocation of loans.
As a result of the taken systemic measures, the number of business entities is increasing (Figure No. 2) and their financial and economic stability is rising.
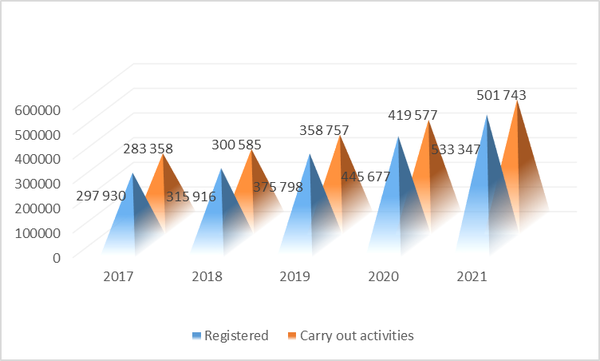
According to the world practice, an unacceptable level of inflation nullifies all the efforts of the state to ensure the well-being of the population. Inflation means rising prices for the social services and goods, depreciation of savings (in national currency) of the population. Therefore, the authorities should implement urgent measures to curb inflation exclusively by market, and not by administrative mechanisms.
Based on this, it is planned that by the end of 2023 the inflation rate will have been reduced up to 5%. The state budget deficit relative to GDP will be no more than 2.5%. Starting from 2022, at least 5% of the budget of each district within the framework of the “Budget for Citizens” program, based on the suggestions by the population, will be directed to solving the most imperious problems.
At the same time, in the context of the national development priorities, the digital economy will become the main driver of the economic growth; its volumes will be increased by at least 2.5 times. The industry of the software products will grow 5 times, the volume of their export – 10 times and will reach $ 500 million. An opportunity will be created to connect each apartment and social institution to the high-speed Internet at affordable prices, and a coverage area for the mobile communications and the Internet will be extended to all main roads. The speed of the international backbone Internet will increase by 5 times, the speed of the inter-district networks – by 8 times.
Based on the principle “The documents move, not the citizens”, by the end of 2022, the office work and the document management with the population in all state bodies will have been fully transferred to electronic form. The share of the public services provided in electronic form will have been increased to 100%.
Thus, the strategy for the development of New Uzbekistan will mark the beginning of a new stage in the national development of the country. The effectiveness of the measures planned by the authorities largely depends on the quality of their implementation in the field and on the accessible communication of their essence and the expected results of the made managerial decisions to the public.
At the same time, the civil society itself should be identified as a key factor in the transformation. Its institutions should be a catalyst for the reforms in the socio-economic sphere, and should also have a decisive role in the assessment of their effectiveness.


